Analysis of the stress state of rocks transformation near a horizontal well during acid treatment based on numerical simulation
- 1 — Ph.D., Dr.Sci. Head of Laboratory Oil and Gas Research Institute, RAS ▪ Orcid
- 2 — Ph.D., Dr.Sci. Head of Department Perm National Research Polytechnic University ▪ Orcid
- 3 — Ph.D., Dr.Sci. Professor China University of Petroleum ▪ Orcid
Abstract
The article presents an overview of the assessment and modelling of the stress state of rocks in the near-wellbore zone of horizontal wells during acid stimulation of the formation for improving the efficiency of oil and gas field development. A numerical finite element model of near-wellbore zone of the reservoir drilled by a horizontal section was compiled using one of oil fields in the Perm Territory as an example. The distribution of physical and mechanical properties of the terrigenous reservoir near the well was determined considering transformation under the action of mud acid for different time periods of its injection. Multivariate numerical simulation was performed and the distribution of horizontal and vertical stresses in near-wellbore zone was determined with regard for different values of pressure drawdown and changes in stress-strain properties depending on the area of mud acid infiltration. It was found that a change in elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio under the influence of acid led to a decrease in stresses in near-wellbore zone. Analysis of the stress distribution field based on the Coulomb – Mohr criterion showed that the minimum safety factor of rock even after the effect of mud acid was 1.5; thus, under the considered conditions of horizontal well modelling, the reservoir rock remained stable, and no zones of rock destruction appeared.
Funding
The work was accomplished under the State assignment “Investigation of properties of oil and gas reservoir systems under physical, geomechanical and physicochemical impact on hard-to-recover hydrocarbon reserves for improving the efficiency of their development” (FMME 2025-0010).
Introduction
Acid treatment of formation is one of the most frequently used enhancement methods for intensifying the inflow of hydrocarbons into the well as well as cleaning the near-wellbore zone from the components of technological fluids used in drilling [1-3]. Despite a high efficiency of this method, it also has disadvantages – under the action of acid reagents, not only the substances clogging the near-wellbore zone, but also the rock matrix minerals dissolve. On the one hand, this effect is manifested in increasing permeability; on the other hand, the chemical interaction of rock and acid should lead to a deterioration in stress-strain properties of reservoir. During acid treatment of a carbonate reservoir the effect of acid usually leads to the appearance of “wormholes” [4-6] and should not significantly affect the wellbore stability, whereas for a terrigenous formation, due to dissolution of intergranular rock cement, a major decrease in Young's modulus and ultimate strength of reservoir rock will occur [7, 8].
When studying acid effect on core samples, the impact of this reagent on permeability is often investigated, and the amount of pore volumes for acid breakthrough and the Damkohler number are determined [4, 6, 9]. At the same time, the effect of acid compositions on physical and mechanical properties of reservoir rocks was not sufficiently investigated. In some articles by foreign experts [9-11] the effect of acid treatment on the dynamic Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio was investigated; however, only carbonate reservoirs and filtration of a small amount of pore volume of acid composition were investigated – prior to its “breakthrough” from the opposite end of samples. At the same time, as shown in publications [12-14] based on the studies of core samples, the porosity and permeability properties of reservoir rock can change not only under the influence of physicochemically active liquids, but also of the changing effective stresses. In this case, the shows of conjugated mechanical and chemical effects will even more intensely transform the natural properties of reservoir rocks (porosity, permeability, physical and mechanical properties, etc.) and affect the stress-strain state of formation, stability of wells and their productivity (injectivity).
When modelling acid action on the formation, the geometry of the forming wormholes and their impact on permeability are usually investigated [15-17] as well as possible chemical reactions of the interaction of reagent with rock minerals [18]. However, the influence of such effects on the stress-strain state of the near-wellbore zone and the destruction of rocks was not sufficiently investigated.
One of the most efficient methods of developing oil and gas fields is the use of horizontal wells [19-21], since in this case the filtration area increases. The use of wells with a horizontal shaft is most efficient in low-permeability reservoirs. This type of wells is most efficiently used in development of low-permeability formations [21-24]; multi-stage hydraulic fracturing cracks are created including the use of acid reagents as fracking fluid [23-25]. Despite the fact that the efficiency of fracking is directly related to a reliable determination of stress-strain properties and the stress state of formation, this problem was virtually not investigated from the viewpoint of joint geomechanical and chemical effects.
Well stability is very important, since wellbore walls can collapse in the process of drilling and operation, which can lead to an emergency when developing oil and gas fields, particularly, for horizontal [26], deep and superdeep wells [27]. To solve this class of problems, 1D geomechanical modelling methods are currently widely used [28-30]. However, this approach has certain disadvantages: stresses are commonly calculated only on wellbore wall, so their distribution at a distance from the wall cannot be determined; well design (column, cement stone) is not taken into account; stress state cannot be calculated near the perforation channels, or perforation holes are considered ideally as cylindrical surfaces [31].
This article based on the numerical finite element method considers how a change in stress-strain properties during acid treatment affects the transformation of stresses in the near-wellbore zone and stability of the open horizontal hole in the terrigenous reservoir. Numerical simulation was performed using the example of a well drilled in one of oil fields in the southern Perm Territory. Mud acid was considered as a reagent, which is quite often used for this type of reservoir, primarily due to its ability to dissolve clay particles [32, 33].
Methodology
Papers [7, 8] present the results of laboratory experiments in which the effect of different numbers of pore volumes of acid reagent on stress-strain properties of core samples taken from a terrigenous reservoir was investigated. Core samples were 6 cm long and 3 cm in diameter. Mud acid, which comprised 12 % hydrochloric acid (HCl) and 3 % hydrofluoric acid (HF), was used as a reagent. During experiments residual water saturation was created in samples, and oil saturation was modelled using kerosene. At the start of the experiment, kerosene was injected into samples, then different pore volumes of acid reagent were filtered, and samples were kept under its influence for 4 h, and at the end of the experiment, kerosene was injected again. As a result of research, it was ascertained that acid treatment of formation led to a decrease in Young's modulus and compressive strength and to an increase in Poisson's ratio (Fig.1).
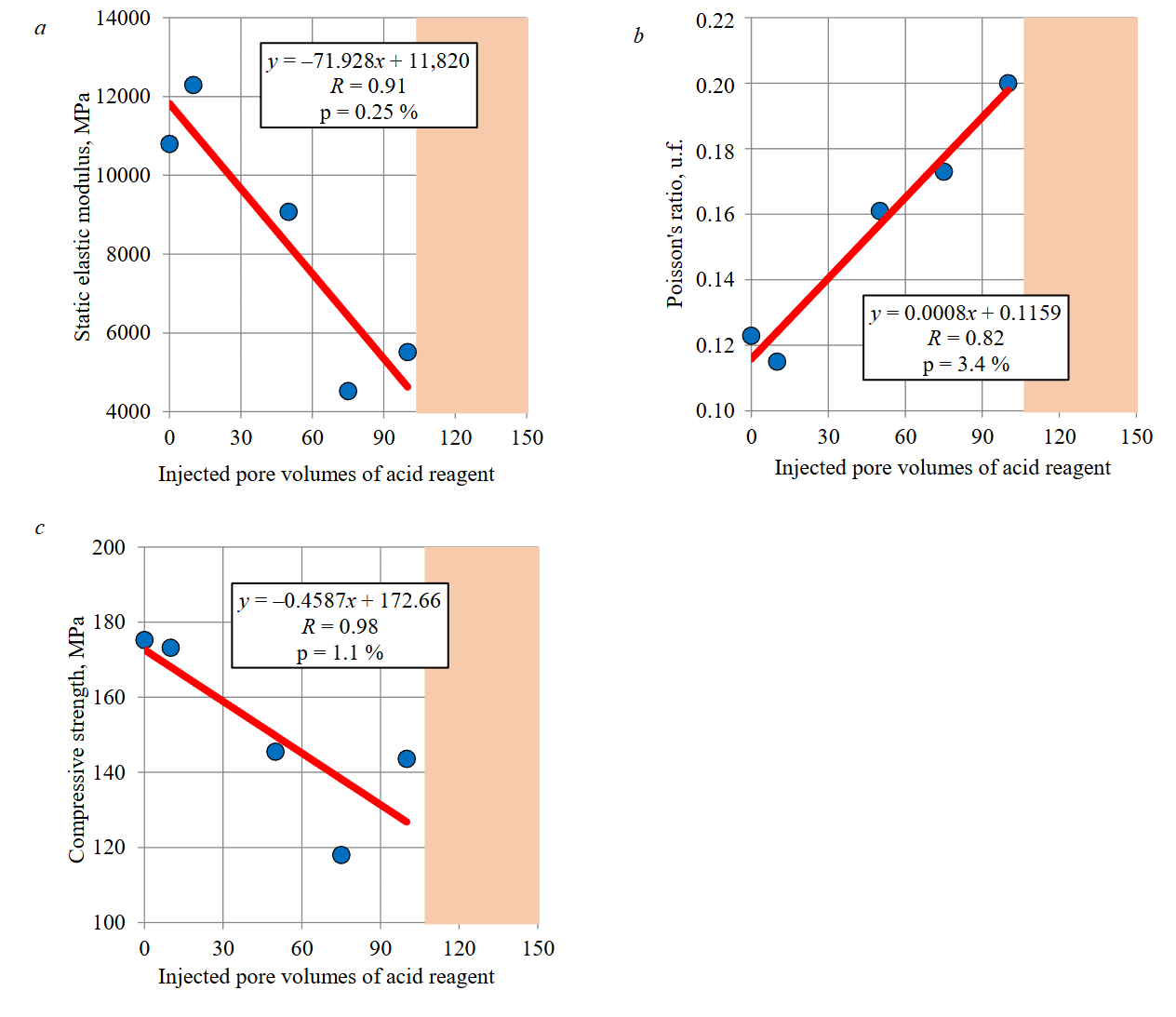
Fig.1. Changes in elastic modulus (a), Poisson's ratio (b) and compressive strength (c) of core samples depending on the number of injected pore volumes of mud acid reagent (zone of sample destruction is shown in pink,
p – dependence significance)
As can be seen from Fig.1, acid treatment resulted in an almost threefold decrease of elastic modulus, 18 % decrease of compressive strength and an approximately twofold increase of the Poisson’s ratio. With increasing number of pore volumes over 100, samples were destroyed after acid filtration; in Fig.1, the area on the graph over 100 pore volumes is highlighted in pink. The significance of dependence is given; its value is less than 5 %, which points to applicability of the ratios used; this is also evidenced by sufficiently high coefficients of their correlations. The dependences in Fig.1 are used for the numerical computation of the stress state of a horizontal well under conditions of acid treatment of the formation.
Numerical simulation was performed in the ANSYS finite element modelling software package [34-36]. This software implements the numerical computation of differential equations describing the poroelastic behaviour of a solid body:
where σ is stress tensor; • – derivative operator; • – divergence operator; σ' – effective stress tensor; α – Biot coefficient; p – pore pressure; I – second-order unit tensor; f – force vector; εV – volumetric strain of rock matrix; Km – Biot modulus; q – fluid flow vector; S – flow source.
The following ratios are also applied for stress and strain relationship:
where εe is strain tensor; D – matrix of elastic constants.
Darcy's law was applied to describe fluid flow in a porous medium:
where k is the second-order permeability tensor; – gradient operator; μ – fluid viscosity.
To calculate the stress field in ANSYS, a finite element model was created using the poroelastic finite element cpt212, including a 20 m thick formation section and an open hole well with a 0.108 m radius (Fig.2). The well was in the centre of reservoir at a depth of 10 m from its roof. Due to the symmetry, only half of the selected section of the near-wellbore zone was considered.
The main physical characteristics of the model for the conditions of the considered terrigenous reservoir in one of oil fields in the southern Perm Territory: elastic modulus of rock without acid treatment is 11.8 GPa; Poisson's ratio of rock without acid treatment 0.116 u.f.; Biot coefficient 0.85 u.f.; angle of internal friction of rock 30 degrees; reservoir depth 1.500 m; vertical stress 33 MPa; horizontal stress 15.8 MPa; reservoir pressure 15.5 MPa; pressure drawdown 1; 5; 10 MPa. Vertical and horizontal stresses were calculated for an average formation occurrence depth of 1,500 m. Since the value of Biot coefficient was not determined in experiments, it was taken as a constant equal to 0.85.
The following boundary conditions were adopted in the numerical model:
- at the lower boundary, displacements in direction of the normal to the surface were fixed (zero displacements along the vertical axis);
- vertical stress was applied to the upper boundary calculated from the formation depth and average density of rocks in the overlying strata equalling 2,200 kg/m3;
- horizontal stress determined from vertical stress and Poisson's ratio of rock was applied to the right lateral surface;
- at the left boundary, due to the symmetry of the model, displacements were fixed in direction of the normal to the surface (zero displacements in horizontal direction).
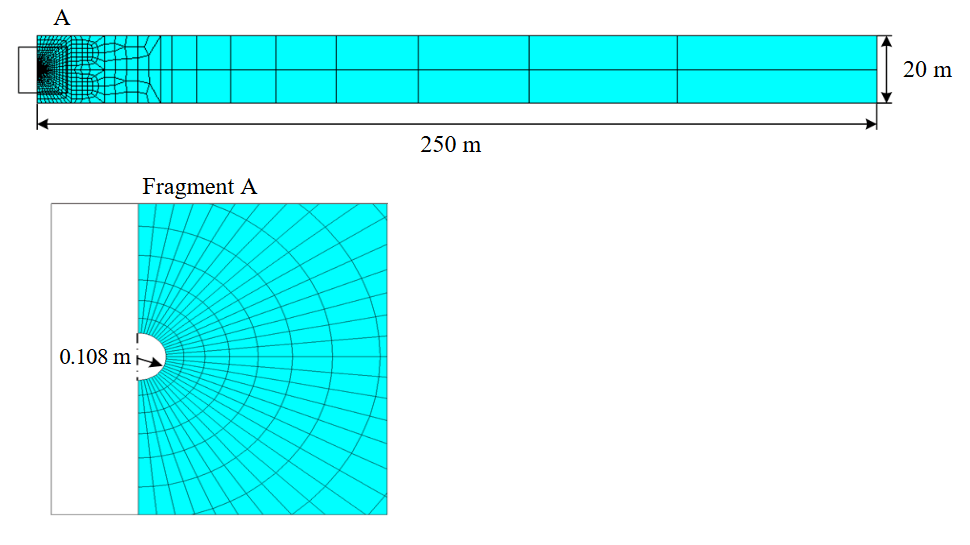
Fig.2. Finite element scheme used to compute the stress state of a horizontal well under conditions of mud acid treatment of formation
Using the compiled finite element model, multivariate numerical computations of the stress state of the near-wellbore zone were accomplished taking into account gradual infiltration of acid into the reservoir. It should be noted that non-stationary filtration of liquid was not calculated, and the distribution area of acid reagent was taken based on data from article [7]. Figure 3 shows how the stress-strain properties of rocks change at different time of filtration and exposure to mud acid. The change in these characteristics takes into account, in addition to filtration time of reagent, its effect when holding samples without filtration for 4 h. In the process of computation, in addition to transformation of physical and mechanical properties, pressure drawdown also varied simulating well operation after acid treatment. Pressure drawdown is 1; 5, and 10 MPa.
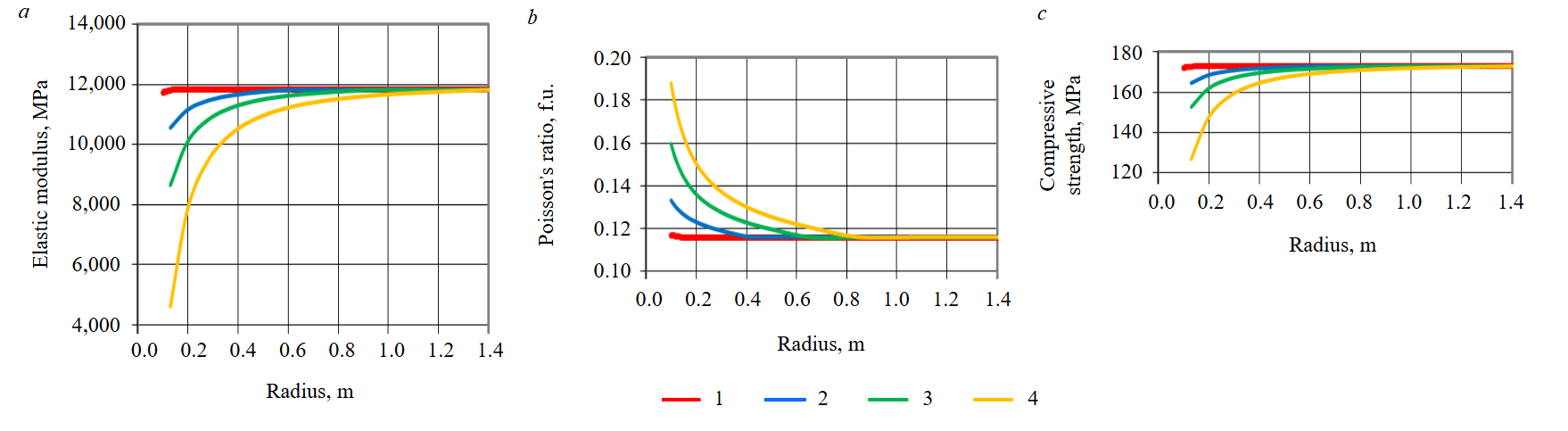
Fig.3. Change in elastic modulus (a), Poisson's ratio (b) and compressive strength (c) depending on radius of distance from well and injection time of mud acid reagent
1 – 14 min; 2 – 4 h, 3 – 9 h; 4 – 32 h
Discussion of results
Figures 4, 5 show the distribution of horizontal and vertical stresses in case of limiting pressure drawdown values (1 and 10 MPa) and mud acid reagent injection time (14 min and 4 h). As can be seen from Fig.4, 5, an increase in pressure drawdown in most computation versions led to the growing values of effective stresses, both horizontal and vertical. At the maximum acid injection time, the maximum values of effective stresses decrease at the same pressure drawdown. The minimum values of effective stresses behave as follows: for the horizontal stress component and pressure drawdown 1 MPa, they increase, at pressure drawdown 10 MPa, decrease; for the vertical component at pressure drawdown 1 and 10 MPa, they decrease.
Analysing Fig. 4, 5, it can be concluded that there is a tendency to stress reduction in near-wellbore zone at acid treatment, which is associated with a change in elastic characteristics of rocks. It should be also noted that at pressure drawdown 1 MPa, the distribution of tensile stresses (negative values) is recorded in the upper and lower parts of the well. Despite the fact that their value is small – a maximum of 1.78 MPa (Fig.4, a), tensile strength of rock can decrease under the influence of acid, which can lead to rock inrushes in these areas.
The next stage involved the assessment of the strength of reservoir rocks near the well based on the Coulomb – Mohr criterion. Fluid pressure in the formation was taken into account in computations, so this criterion was written as follows:
where σ1, σ3 are the principal maximum and minimum stresses; USC – ultimate strength of rock under uniaxial compression; φ – angle of internal friction; p – formation pressure.
Fig.6 shows the results of determining the safety factor of reservoir rocks based on the Coulomb – Mohr criterion at pressure drawdown 1; 5, and 10 MPa for different time of reagent injection. If this factor is higher than 1, this points to rock stability; if it is less than 1, then its destruction is likely.
Computation results showed that for the simulated conditions, the destruction of reservoir rocks should not occur, although the minimum safety factor is 1.5, i.e. rocks are close to destruction. As can be seen from Fig.6, the area with the lowest safety factor lies near the lateral surface of the well, which is caused by the effect of vertical stresses, which are much higher than the horizontal ones. A decrease in elastic properties due to the action of mud acid reagent led to a decrease in stresses
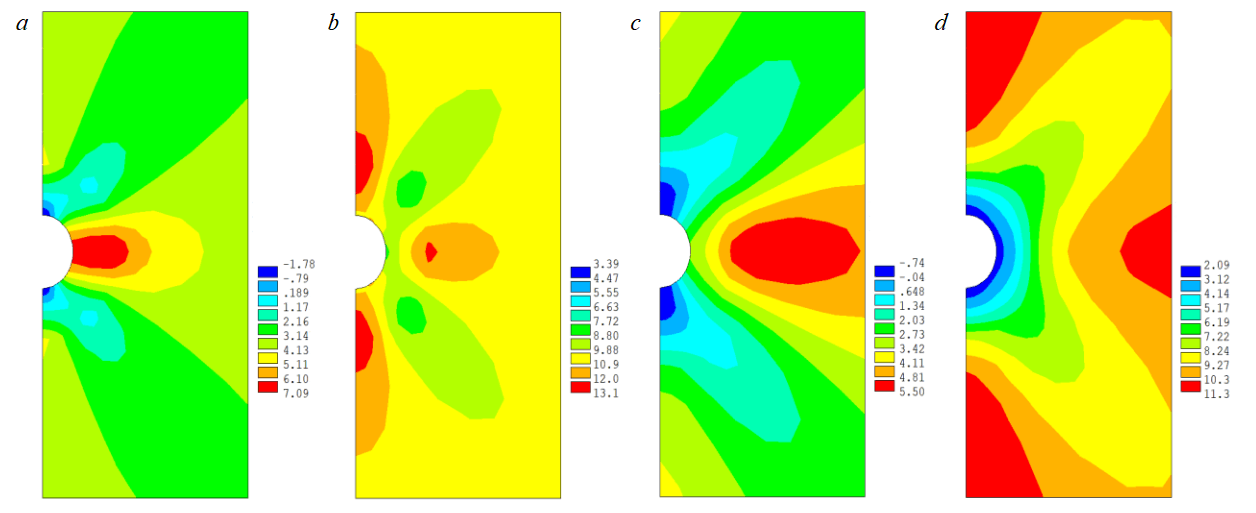
Fig.4. Distribution of horizontal effective stresses at pressure drawdown 1 (a, c) and 10 (b, d) MPa after injection of mud acid reagent for 14 min (a, b) and 4 h (c, d)
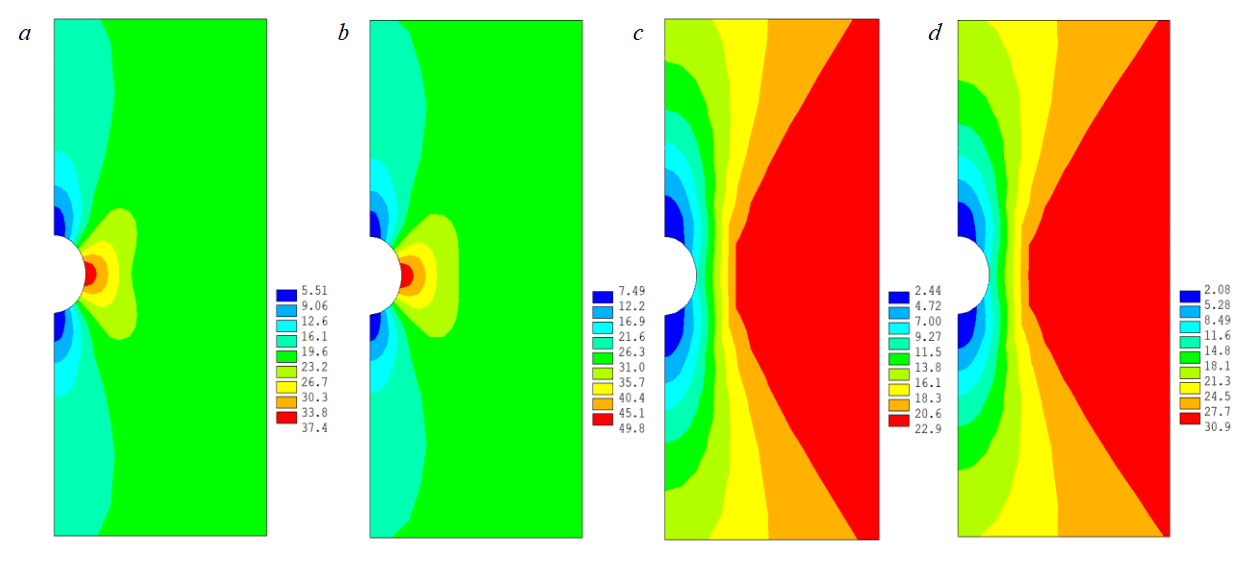
Fig.5. Distribution of vertical effective stresses at pressure drawdown 1 (a, c) and 10 (b, d) MPa after injection of mud acid reagent for 14 min (a, b) and 4 h (c, d)
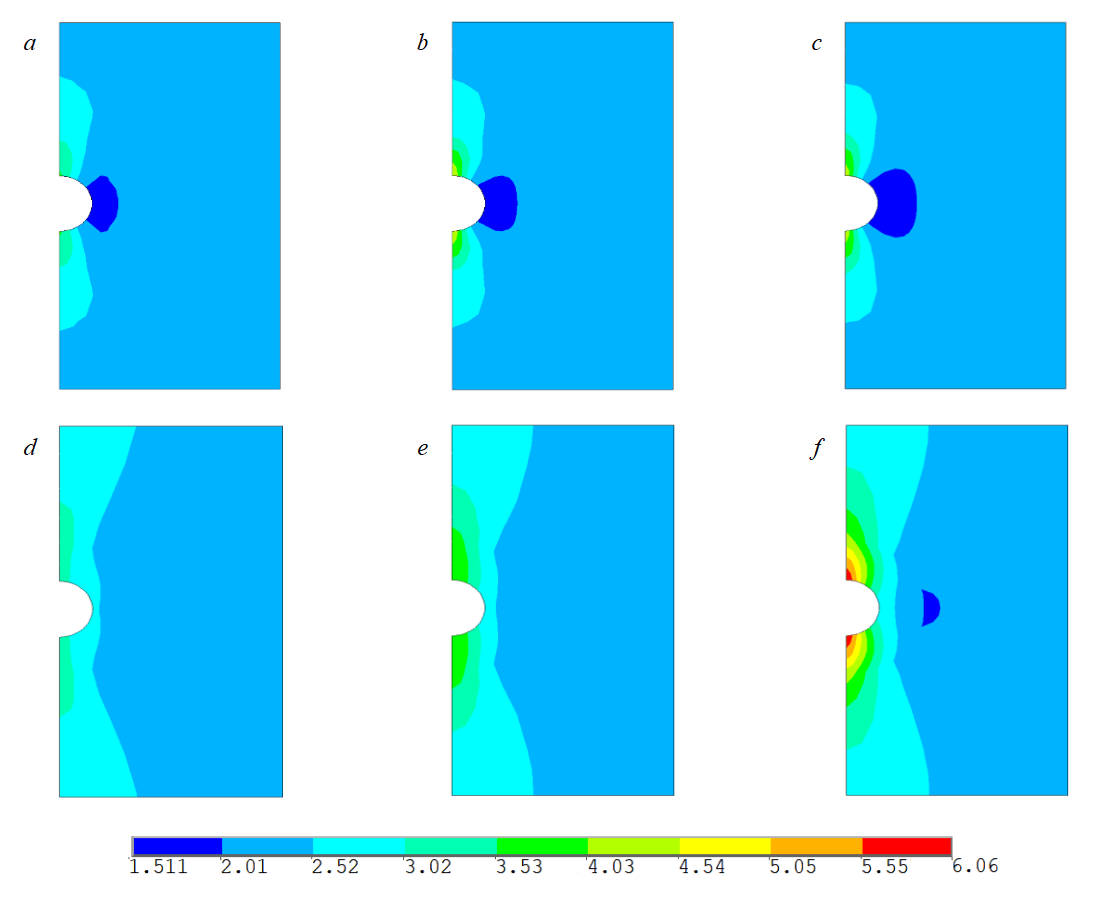
Fig.6. Distribution of rock safety factor near the well for pressure drawdown 1 (a, d), 5 (b, e) and 10 (c, f ) MPa after injection of mud acid reagent for 14 min (a, b, c) and 4 h (d, e, f )
and an increase in safety factor, especially in the upper and lower parts of the well (Fig.6, f), while an increase in pressure drawdown value led to an increase in this parameter in the areas under consideration and a decrease in the lateral area of the well.
In the course of further investigation of this problem it is planned to compare field data on horizontal wells in which mud acid treatment will be conducted to assess the probability of sand ingress depending on exposure time and volumes of reagent injection, as well as changes in permeability in the near-wellbore zone.
The investigation results can be applied to terrigenous reservoir rocks of the Tulskii and Bobrikovskii producing formations in the southern group of fields in the Perm Territory with similar porosity and permeability, physical and mechanical properties. Difference in permeability values leads to a change in acid filtration area depending on time, and the difference in initial mechanical properties will lead to other ratios describing the relationship of their change depending on the injected pore volumes of reagent, which can require additional laboratory and numerical experiments.
Conclusion
Using the example of a terrigenous reservoir in one of oil fields in the southern Perm Territory, the analysis of the stress state of reservoir near the open hole of a horizontal well was conducted taking into account the transformation of the stress-strain properties of rocks under the action of mud acid reagent. Based on results of analysis, the following main conclusions can be drawn:
- As part of this work, the numerical finite element model of a region of terrigenous formation was compiled including an open hole of a horizontal well and allowing for changes in stress-strain properties of reservoir rocks during mud acid treatment.
- Using the compiled model, a multivariate numerical simulation of the stress state of reservoir was accomplished for different values of pressure drawdown and filtration time of mud acid reagent.
- Analysis of stress distribution field showed that an increase in pressure drawdown led to increasing values of effective stresses in reservoir, while the consequence of a change in elastic properties of rocks under the influence of acid was, on the contrary, their decrease.
- Based on application of the Coulomb – Mohr criterion, the distribution of rock safety factor was determined, which showed that the reservoir was in a stable state both without the effect of mud acid, and with treatment of the near-wellbore zone with this reagent. At the same time, an increase in pressure drawdown led to a decreasing rock safety factor, and the effect of acid led to its increase.
- The numerical model compiled as part of the work can be used to calculate the stress distribution field near horizontal wells for other types of reservoirs, both considering and without considering the change in stress-strain properties under the action of not only mud acid reagent, but also different other physicochemically active liquids.
References
- Peifeng Jia, Chuanzhi Cui, Yingfei Sui et al. Uniform Acid Cleaning Technology and Its Application in Horizontal Wells with Open Hole Screen Tube. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2023. Vol. 2594. N 012052. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/2594/1/012052
- Ganiev Sh.R., Lysenkov A.V., Gafarov Sh.A. Development of an algorithm for wells and technologies selection for hydrochloric acid treatment of carbonate oil-saturated reservoirs in the Republic of Bashkortostan. Oil Industry Journal. 2021. N 2, p. 77-81 (in Russian). DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2021-2-77-81
- Krivoshchekov S.N., Kochnev A.A., Ravelev K.A. Development of an algorithm for determining the technological parameters of acid composition injection during treatment of the near-bottomhole zone, taking into account economic efficiency. Journal of Mining Institute. 2021. Vol. 250, p. 587-595. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2021.4.12
- Al-Arji H., Al-Azman A., Le-Hussain F., Regenauer-Lieb K. Acid stimulation in carbonates: A laboratory test of a wormhole model based on Damköhler and Péclet numbers. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. 2021. Vol. 203. N 108593. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108593
- Yifan Dong, Yu Lei, Ting Jin et al. Optimized Acidizing Stimulation Technology Achieves Production Increase in Ultra-High Temperature Carbonate Reservoirs. SPE International Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, 12-14 September 2023, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman. OnePetro, 2023. N SPE-215682-MS. DOI: 10.2118/215682-MS
- Alameedy U., Fatah A., Abbas A.K., Al-Yaseri A. Matrix acidizing in carbonate rocks and the impact on geomechanical properties: A review. Fuel. 2023. Vol. 349. N 128586. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128586
- Popov S.N., Smetannikov O.Yu. Numerical simulation of permeability and stress-strain state change of the near-well zone of a productive reservoir under the combined action of acid composition and varying effective stresses. Geology, geophysics and development of oil and gas fields. 2017. N 12, p. 45-53 (in Russian).
- Plotnikov V.V., Rehachev P.N., Barkovsky N.N. et al. The Effect of Acid Treatments on the Bottom Zone of Clastic Reservoir Rocks of Perm Region. SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference and Exhibition, 24-26 October 2016, Moscow, Russia. OnePetro, 2016. N SPE-182063-MS. DOI: 10.2118/182063-MS
- Mustafa A., Alzaki T., Aljawad M.S. et al. Impact of acid wormhole on the mechanical properties of chalk, limestone, and dolomite: Experimental and modeling studies. Energy Reports. 2022. Vol. 8, p. 605-616. DOI: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.11.249
- Alameedy U., Alhaleem A.A., Isah A. et al. Effect of acid treatment on the geomechanical properties of rocks: an experimental investigation in Ahdeb oil field. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology. 2022. Vol. 12. Iss. 12, p. 3425-3441. DOI: 10.1007/s13202-022-01533-x
- Jahani N., Berge G., Haugen B. Prediction of Rock Strength with Matrix Acidizing Stimulation and Induced Wormhole by Computational Simulation Methods. ISRM Regional Symposium – EUROCK 2014, 27-29 May 2014, Vigo, Spain. OnePetro, 2014. N ISRM-EUROCK-2014-213.
- Zhukov V.S., Kuzmin Yu.О. Comparison of the approaches to assessing the compressibility of the pore space. Journal of Mining Institute. 2022. Vol. 258, p. 1008-1017. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2022.97
- Petrakov D.G., Penkov G.M., Zolotukhin A.B. Experimental study on the effect of rock pressure on sandstone permeability. Journal of Mining Institute. 2022. Vol. 254, p. 244-251. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2022.24
- Karev V.I., Kovalenko Yu.F., KhimuliaV.V., Shevtsov N.I. Parameter determination of the method of directional unloading of the reservoirbased on physical modelling on a true triaxial loading setup. Journal of Mining Institute. 2022. Vol. 258, p. 906-914. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2022.95
- Turegeldieva K.A., Zhapbasbayev U.K., Assilbekov B.K., Zolotukhin A.B. Matrix acidizing modeling of near-wellbore with reduced reservoir properties (part 2). Oil Industry Journal. 2016. N 4, p. 108-110 (in Russian).
- Deng J., Mou J., Hill A.D., Zhu D. A New Correlation of Acid-Fracture Conductivity Subject to Closure Stress. SPE Production & Operation. 2012. Vol. 27. Iss. 2, p. 158-169. DOI: 10.2118/140402-PA
- Mingwei Wang, Wen Zhou, Song Li, Wen Wu. Simulated Investigation in Wormhole Expansion Law of Gelling Acid Etching and Its Influencing Factors in Deep Carbonate Reservoirs. Gels. 2022. Vol. 8. Iss. 8. N 470. DOI: 10.3390/gels8080470
- Khasanov М.М., Maltcev А.А. Modeling the acid treatment of a polymictic reservoir. Journal of Mining Institute. 2021. Vol. 251, p. 678-687. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2021.5.7
- Suleymanova M.V., Trofimchuk A.S., Khabibullin G.I. Experience of horizontal injection wells application in the development of terrigenous reservoir of RN-Yuganskneftegas LLC fields. Oil Industry Journal. 2023. N 1, p. 23-27 (in Russian). DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2023-1-23-27
- Deryaev A.R. Well trajectory management and monitoring station position borehole. SOCAR Proceedings. 2023. Special Issue N 2, p. 1-6 (in Russian). DOI: 10.5510/OGP2023SI200870
- Murtazin R.R., Aksakov A.V., Yamilev I.M. et al. The study of multiple hydraulic fractures propagation along the horizontal wellbore. Oil Industry Journal. 2023. N 2, p. 90-94. DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2023-2-90-94
- Osorgin P.A., Kashapov A.A., Egorov E.L. et al. Development of low-permeable terrigenous reservoirs using horizontal wells with multiple hydraulic fractures at Priobskoye license area of RN-Yuganskneftegas LLC. Oil Industry Journal. 2023. N 6, p. 38-43 (in Russian). DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2023-6-38-43
- Li W., Chen L., Wang X. et al. Acid Fracturing Technology and Effect Evaluation of Carbonate Horizontal Well in Fuman Oilfield. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2024. Vol. 2679. N 012010. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/2679/1/012010
- Fei Liu, Yu Fan, Li Li et al. Case Study of Successfully Staged Acid Fracturing on the Ultra-Deep Horizontal Well for the Qixia Fm HTHP Tight Carbonate Gas Reservoir in China. Frontiers in Energy Research. 2022. Vol. 10. N 917740. DOI: 10.3389/fenrg.2022.917740
- Safari R., Smith C., Fragachan F. Improved Recovery of Carbonate Reservoir by Optimizing Acidizing Strategy; Coupled Wellbore, Reservoir, and Geomechanical Analysis. Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, 13-16 November 2017, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. OnePetro, 2017. N SPE-188683-MS. DOI: 10.2118/188683-MS
- Kozyrev A.S., Ermolaev N.I., Mishin A.V. et al. Engineering solutions for horizontal wellbore stabilization in the presence of coal deposits. Oil Industry Journal. 2023. N 4, p. 28-33 (in Russian). DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2023-4-28-33
- Dvoynikov M.V., Sidorkin D.I., Yurtaev S.L. et al. Drilling of deep and ultra-deep wells for prospecting and exploration of new raw mineral fields. Journal of Mining Institute. 2022. Vol. 258, p. 945-955. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2022.55
- Lutfullin A.A., Girfanov I.I., Usmanov I.T., Sotnikov O.S. Software for geomechanical simulation. Oil Industry Journal. 2021. N 7, p. 49-52 (in Russian). DOI: 10.24887/0028-2448-2021-7-49-52
- Tappi N., Cherdasa J.R. 1D Geomechanical Model For Wellbore Stability in Z Field, Y Well Sanga Sanga Working Area, Kutai Basin. Journal of Geoscience, Engineering, Environment, and Technology. 2023. Vol. 8. N 02-2, p. 72-84. DOI: 10.25299/jgeet.2023.8.02-2.13871
- Linsheng Wang, Xinpu Shen, Baocheng Wu et al. Integrated Analysis of the 3D Geostress and 1D Geomechanics of an Exploration Well in a New Gas Field. Energies. 2023. Vol. 16. Iss. 2. N 806. DOI: 10.3390/en16020806
- Fallahzadeh S.H., Shadizadeh S.R., Pourafshary P., Zare M.R. Modeling the Perforation Stress Profile for Analyzing Hydraulic Fracture Initiation in a Cased Hole. Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, 31 July – 7 August, 2010, Tinapa – Calabar, Nigeria. OnePetro, 2010. N SPE-136990-MS. DOI: 10.2118/136990-MS
- Magadova L.A., Sirotin A.N., Pakhomov M.D., Davletov Z.R. The Analysis of the Dissolving Ability of Fluorine-Containing Acid Compositions against Silicate Components of Terrigenous Formation. Oil and Gas Territory. 2020. N 7-8, p. 72-80 (in Russian).
- Magadova L.A., Davletshina L.F., Pakhomov M.D., Davletov Z.R. Generation of sedimentation in the interaction with acid compositions of a terrigene reservoir. Oilfield engineering. 2015. N 9, p. 31-36 (in Russian).
- Chernyshov S.E., Popov S.N., Varushkin S.V. et al. Scientific justification of the perforation methods for Famennian deposits in the southeast of the Perm Region based on geomechanical modelling. Journal of Mining Institute. 2022. Vol. 257, p. 732-743. DOI: 10.2118/206161-PA
- Jiecheng Zhang, Moridis G., Blasingame T. Message Passing Interface (MPI) Parallelization of Iteratively Coupled Fluid Flow and Geomechanics Codes for the Simulation of System Behavior in Hydrate-Bearing Geologic Media. Part 1: Methodology and Validation. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering. 2022. Vol. 25. Iss. 03. p. 600-620. DOI: 10.2118/206161-PA
- Kharlamov S.N., Janghorbani M., Zaykovskiy V.V. Transportation of cuttings by drilling mud in horizontal wells. Part 1. Modeling the structure of dispersed currents. Bulletin of the Tomsk Polytechnic University. Geo Аssets Engineering. 2023. Vol. 334. N 10, р. 34-48 (in Russian). DOI: 10.18799/24131830/2023/10/4433
