Assessment of the efficiency of acid mine drainage purification (using the example of copper-pyrite mines in the Middle Urals)
Abstract
According to the results of the anti-rating of regions with extreme pollution of watercourses in the Sverdlovsk region, the largest number of polluted rivers has been recorded in recent years – more than a quarter of all high and extremely high pollution. One of the sources of pollution of natural water bodies in the Middle Urals are closed and flooded copper-pyrite mines, where acidic mine drainage continue to form and unload to the surface. Several of them have organized collection and a two-stage acidic drainage purification system, including neutralization with lime milk and settling in a clarifier pond. Despite the identical schemes, different indicators of pollutants are recorded during discharge into water bodies. The aim of the work is to evaluate the effectiveness of the applied acid mine drainage purification system and identify the parameters affecting the quality of treated mine water. Laboratory studies were performed using methods of flame emission spectrometry, flame atomic absorption, atomic absorption spectrometry, mass spectrometry with ionization in inductively coupled plasma, potentiometric, etc. It has been established that the existing mine drainage purification system at the Degtyarskii mine makes it possible to significantly reduce the concentrations of most toxic components of mine waters to almost standard values. At the Levikhinskii mine, the multiplicity of exceeding the maximum permissible concentrations reaches hundreds and thousands of times. To achieve a higher degree of purification, it is necessary that the duration of passive purification is sufficient for the reactant to interact with acidic waters. However, to ensure this possibility, it will require the creation of a cascade of ponds with an area of several thousand hectares. If the current two-stage system is quite effective for the Degtyarskii mine, then for Levikhinskii it is necessary to switch to the use of more modern systems, including three stages of purification.
Funding
The work was performed within the framework of the state assignment of the Institute of Mining of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences N 075-00412-22 AVE. Topic 2 (2022-2024) “Development of geoinformation technologies for assessing the security of mining territories and forecasting the development of negative processes in subsurface use” (FUWE-2022-0002) N 1021062010532-7-1.5.1
Introduction
Acid mine drainages (AMD) is one of the most serious environmental problems, closely related to mining activities. The main reason for the formation of these waters is the presence of sulfide minerals in rocks [1, 2]. During mining, the integrity of the rock mass is violated, sulfuric acid weathering of sulfide minerals occurs when interacting with water and air, which leads to the formation of acid mine drains [3-5]. Low pH values in mine waters contribute to the further dissolution of minerals and the release of heavy metals from them. These flows, when entering the landscapes of mining territories, cause significant damage to both the hydrosphere and the entire environment as a whole [6-8].
The main problem with AMD purification is their high acidity (pH = 2.5-4.5), the presence of dangerous chemical elements (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Al), as well as large volumes of water that are formed after flooding of mines and come to the surface for tens and sometimes hundreds of years [9]. The composition of mine waters depends on the time that has passed since the flooding. In the first years, there is a sharp increase in all indicators, sometimes 3-5 times compared to the stage of development. This phenomenon is called the “first flush” and manifested itself, among other things, in the copper-pyrite mines of the Middle Urals [2, 10]. In the future, there is a gradual rather slow decline in mineralization and concentrations of individual components, but at the same time significant fluctuations in their content are noted depending on the season and the water content of the period. These processes significantly complicate the organization of mine water purification and must be taken into account at each specific facility.
In the Sverdlovsk region, at many liquidated copper-pyrite mines (Levikhinskii, Karpushikhinskii, Lomovskii, Degtyarskii, etc.), after the cessation of drainage, concentrated AMD outlets formed, as a rule, in the lowest part of the mining landscape (in sinkholes, pits). Although their consumption is lower than during mining and mine drainage, it can reach several thousand cubic meters per day and, without cleaning, leads to degradation of the landscape and unacceptable pollution of the hydrosphere over significant areas. To prevent environmental pollution of such facilities, since the early 2000s, AMD collection and neutralization has been organized at the expense of the regional budget (for this purpose, the State Government Institution of the Sverdlovsk region “Uralmonatsit” was created). Treated wastewater from the Levikhinskii, Karpushikhinskii and Lomovskii mines is discharged into the Tagil River (Irtysh basin district), below the discharges is the Lenevskii reservoir, which is one of the sources of water supply in Nizhnii Tagil (population 350 thousand people) [11]. Despite the cleaning, the level of water pollution in the mouth of the Levikha River exceeds the permissible norms by thousands and hundreds of times [12].
The Degtyarskii copper-pyrite deposit is located on the eastern slope of the Middle Urals in the municipal district of Degtyarsk, Sverdlovsk region, 45 km southwest of Yekaterinburg, 18 km southeast of Revda. The deposit was mined from 1914 to 1995. The operation was carried out comprehensively by both open and underground methods up to a depth of 610 m. At the end of 1995, due to the liquidation of the mine, the mine drainage was stopped and by 1999 the filling of the depression funnel was completed [13]. From this moment on, AMD with a flow rate of about 180 m3/h enters the pit hole of the Kolchedannaya mine in the northern part of the field. AMD flowing from the pit enters the Istok River in a dispersed flow, where it is mixed with lime milk, which is piped from the neutralization station. Then the entire runoff of neutralized mine waters along the riverbed enters the Yelchevskii pond sump, built in 1952 to purify the mine waters of an operating mine [14-16]. The design volume of the pond is 9.4 million m3, with an area of 220 ha [17]. After settling, the water purified from suspension along the riverbed of the Yelchevka River enters the Volchikhinskii reservoir, which is the main source of drinking water supply in Yekaterinburg (population 1.5 million people) (Fig.1) [18].
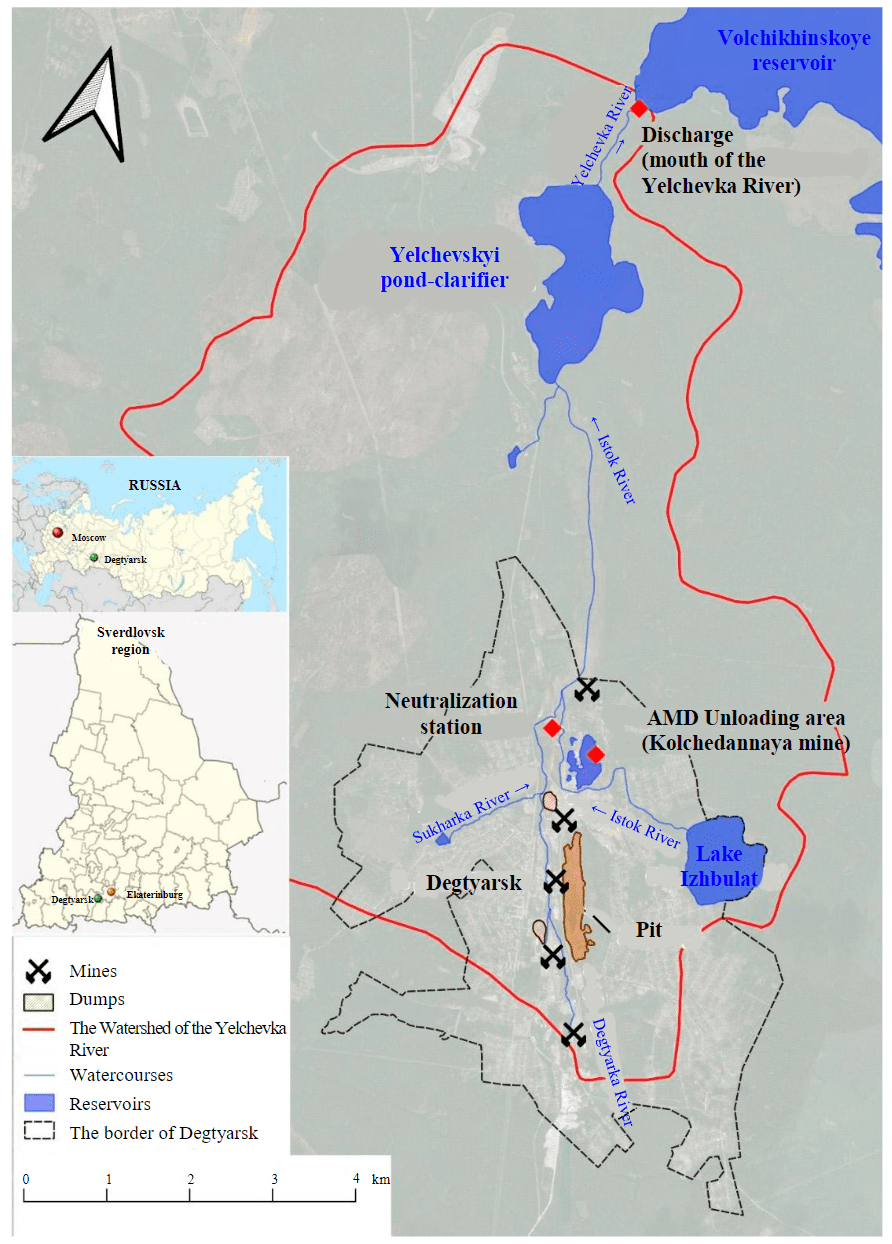
Fig.1. Overview map of the location of facilities at the Degtyarsk mine
The degree of purification is much higher here, almost up to the standards of maximum permissible concentrations (MPC). The Volchikhinskoe reservoir is located in the basin of the Chusovaya River (Kama basin District), Yekaterinburg is located on the Iset River (Irtysh Basin District). In fact, the inter-basin transfer of river flow through the Main Ural watershed is carried out. Water from the Volchikhinskoe reservoir is supplied to Yekaterinburg, providing the bulk of the city's domestic water supply, therefore, the state of the hydrosphere in the watershed of the Volchikhinskoe reservoir is the subject of close attention by both supervisory authorities and the public.
The Levikhinskoe copper-pyrite deposit is located 120 km north of Yekaterinburg, on the eastern outskirts of the village Levikha, 30 km northwest of Kirovgrad (Fig.2). The mine was worked out from 1927 to 2003 both open and underground to a depth of 615 m. Until the end of the 1950s, AMD was dumped into the Porokhovoe swamp, located in the north-west of the deposit, without preliminary purification. In 1959, a clarification pond was built in the valley of the Levikha River. Its design volume is 3 million m3, its area is 142 ha. In 2003, the drainage was stopped, which led to the filling of the depression funnel, and by 2007, a man-made reservoir was formed at the lowest point of the mining outlet in the sinkhole of the Levikha II mine, into which AMD is discharged. The discharge flow rate is approximately 115 m3/h, which is half what it was during the mining period. Mine water is pumped through a pipeline from a man-made reservoir in the area of the Levikha II mine to a neutralization station. After adding lime milk, these waters enter the clarifier pond, and then flow by gravity along the old riverbed of the Levikha River into the Tagil River (Fig.2).
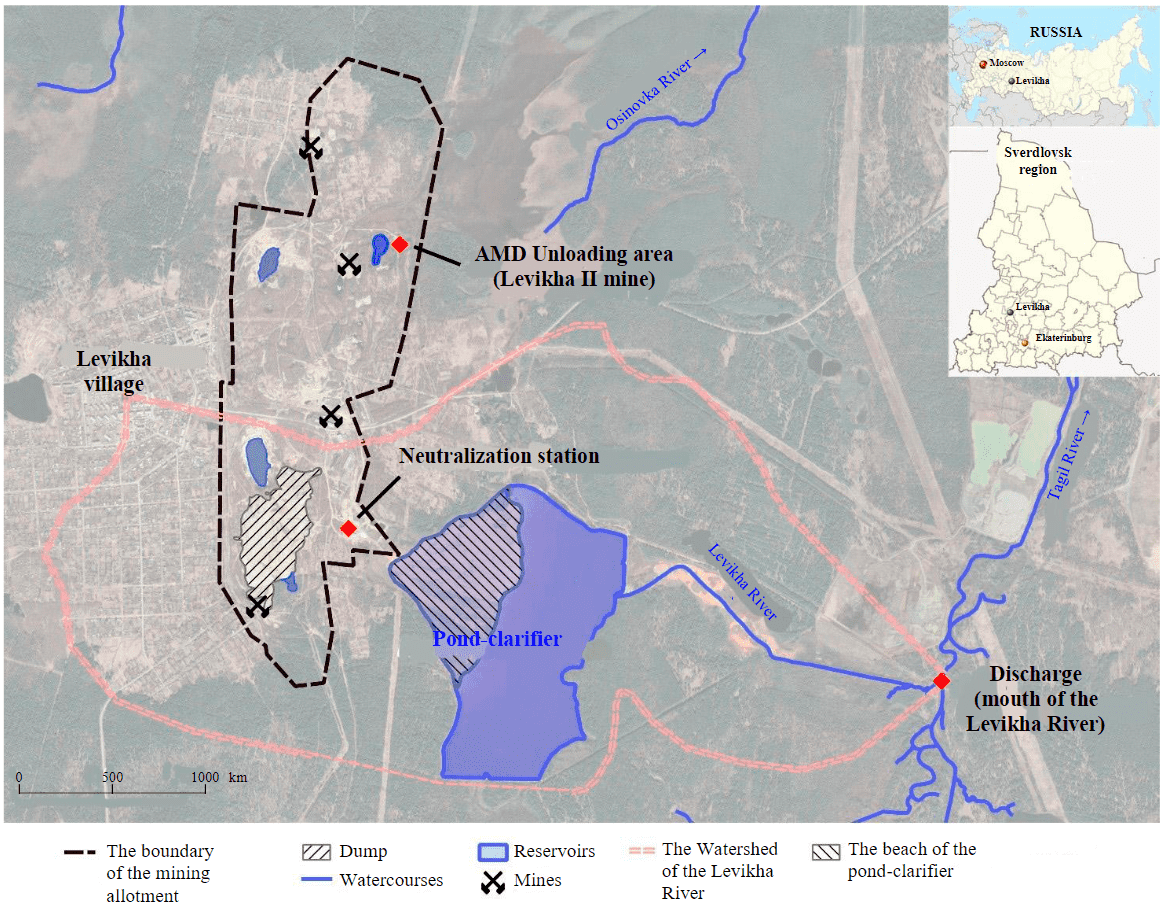
Fig.2. Overview map of the location of facilities at the Levikhinskii mine
A wide variety of technologies are currently used to effectively clean AMD, in general they are divided into active and passive methods [19-21].
Active purification methods are chemical (neutralization), electrochemical, membrane, ion exchange, sorption, oxidation, eutectic crystallization by freezing [22-24]. Active cleaning systems require various equipment (tanks, mixers, pumps and aerators), regular maintenance, continuous dosing of chemicals, and power supply. The main advantages of their use include: effective removal of contaminants from mine drains, precise process control, allowing them to be designed and operated to obtain water of a certain chemical composition, as well as the possibility of use in places with a limited area. The main limitations are the high capital and current costs of operation and maintenance. Active cleaning is more suitable for operating mines, which usually have a subsurface area for extraction, as well as production facilities and personnel to manage the cleaning system.
In order to increase the pH of mine waters, reduce the solubility of pollutants, control the composition of wastewater and reduce the harm caused to the environment by acidic waters, substances such as limestone CaCO3, slaked lime Ca(OH)2, quicklime, or calcium oxide CaO, liquid and solid caustic soda NaOH are used as reagents, soda ash Na2CO3, ammonia NH3 [25]. A certain chemical is suitable for a specific state and conditions. The choice of a specific reagent depends on both technical (pH level, consumption, metal concentration) and economic factors (reagent price, labor, equipment, cleaning time) [26-28].
Passive purification systems are based on natural physical, geochemical and biological processes. These can include: limestone drains or channels, wetlands, systems for reducing and increasing alkalinity, clarification ponds, passive oxidation systems (cascades) [17, 29].
Unlike active methods, which require a continuous supply of reagents to neutralize the acidity of mine waters during the entire period of operation, passive systems are usually designed with such a service life (25 years) of the neutralizing material that no additional costs are required during this period [30]. Most passive systems are based on dissolving a neutralizing material (usually limestone) to increase the pH. In order to effectively interact pollutants with reagents, sufficient residence time in systems is necessary; therefore, large areas of land are usually necessary for the implementation of passive systems [31-33]. The combination of active and passive methods leads to a significant increase in the degree of purification. The most cost-effective and highly effective combination of methods is, for example, the use of reagents to reduce acidity and sedimentation of mine waters in clarification ponds before discharge into water bodies.
The aim of this work is to evaluate the efficiency of AMD purification at facilities in the Middle Urals and identify the main parameters that allow achieving higher water quality indicators at discharge into water bodies. To do this, the following tasks were solved: an array of hydrochemical monitoring data was processed at the Degtyarskii and Levikhinskii mines as the most significant objects; the efficiency of the AMD purification system was evaluated; the main factors on which the reduction of pollution indicators depends were identified, and measures for organizing cleaning at the Levikhinskii mine were proposed.
Research methods
To analyze the chemical composition of water in the area of Degtyarskii and Levikhinskii copper-pyrite mines, monitoring data was used, which was conducted by Uralmonatsit in Degtyarsk and the village Leviha. At these facilities, the most characteristic pollution indicators for AMD are determined monthly (starting from the moment AMD reaches the surface) in the discharge zone and when wastewater is discharged into surface reservoirs: hydrogen index, copper, zinc, total iron, suspended solids, total mineralization (dry residue), chlorides, sulfates, manganese, petroleum products, and arsenic.
The Institute of Mining of the Ural Branch of the RAS has tested an expanded list of components. The analyses were carried out at the Institute of Industrial Ecology of the Ural Branch of the RAS (Yekaterinburg) using methods of flame emission spectrometry (determination of Na, K), flame atomic absorption spectrometry (Ca, Mg), atomic adsorption spectrometry (Fe), mass spectrometry with ionization in inductively coupled plasma (Al, Be, Cd, Co, Mn, Cu, As, Ni, Pb, Se, Zn), determination of nitrogen-containing substances (NO2), potentiometric with ion-selective electrode (NO3), gravimetric (SO4) and argentometric (Cl), photometric in the form of yellow silica-molybdenum heteropolyacid (Si), determination of alkalinity and mass concentration of carbonates and hydrocarbonates. About 16 components were found in each sample. T (°C), Eh (mV), pH, TDS (mg/l), EC (mSm/cm) were measured on site.
To visualize the results of the chemical composition of water and display a variety of indicators, classifications based on Piper and Durov diagrams are most often used. Such graphs are based on the same principle of construction – the image of the sample with two points on two Ferre triangles. The diagrams use three main cations Са2+, Mg2+, Na+ (in our case, the content of Na+ is insignificant, therefore Fe+Al3+ are taken into account) and three main anions HCO3–, SO42–, Cl–. The triangles show the dominant number of cations and anions, and the field shows the classification of the sample. The main difference between the Durov diagram is that it includes the hydrogen index and mineralization. Guided by considerations of unification, visualization and detection of trends in changes in the chemical composition and indicators of water, a classification based on the Durov diagram was chosen for plotting in the work.
The efficiency of the system was evaluated using the formula:
where Сin, Сout are the concentrations of pollutants in the AMD discharge zone and in wastewater at the mouth of the Yelchevka and Levikha rivers, respectively, mg/l.
To calculate the required volume of an alkaline reagent that will neutralize hydrogen ions, both present in the solution (pH of the solution) and formed during the oxidation of soluble metals and their precipitation, the water acidity formula is used1 [34]:
where the calculated acidity is expressed in mg/l CaCO3; Fe2+, Fe3+, Al3+, Mn2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ – metal concentrations in solution, mg/l; 50 – the coefficient for converting mg-eq of acidity to mg/l CaCO3; The content of Fe2+ and Fe3+ was calculated using the PHREEQC computer program2.
To assess the degree of exposure of a group of pollutant components, a total pollution indicator is used3:
where Ci – the actual content of the substance determined in water, mg/l; СMPC – MPC of pollutants for fishery purposes; n – the number of defined summable substances.
The dependence [22] is used to estimate the area of the cascade of ponds necessary for passive purification and sedimentation of water after neutralization
where F – required pond area, m2; Qd – average daily water consumption, m3/day; Ct – concentrations of pollutants at final discharge, mg/l; Ra – the rate of removal of pollutants, g/m2/day.
Results discussion. To assess the effectiveness of mine water treatment, comparative dates were taken – 10 years after the stop of drainage – 2003-2004 at the Degtyarskii, 2015-2016 and Levikhinskii mines. The mine waters at the Degtyarsk mine in the unloading zone (here a man-made reservoir was formed in the pit of the Kolchedannaya mine) are characterized as acidic (pH = 2.3-3.3), Eh = 263 mV, sulfate in anionic composition, aluminum-iron-calcium-magnesium cationic (the order of cations is not constant), mineralization M it varies from 1.4 to 16 g/l (Tables 1, 2, Fig.3). At the Levikhinskii mine in the unloading zone (in a technogenic reservoir in the sinkhole of the Levikha II mine), the waters are less acidic (pH = 3.6-3.9), Eh = 188 mV, calcium-magnesium-iron-aluminum sulfate in composition (the ratio of cations may vary), with mineralization from 14.2 to 20.0 g/l.
Table 1
Results of hydrochemical monitoring
|
Indicators |
MPC |
AMD Unloading area |
Discharge |
Cleaning efficiency, % |
||||
|
fi* |
dw** |
Degtyarskii mine |
Levikhinskii mine |
The mouth of the Yelchevka River |
The mouth of the Levikha River |
Degtyarskii mine |
Levikhinskii mine |
|
|
рН |
6.5-8.5 |
6.0-9.0 |
2.3-3.3*** 2.6 |
3.6-3.9 3.8 |
7.2-7.5 7.4 |
6.6-7.6 7.2 |
– |
– |
|
Fetotal, mg/l |
0.1 |
0.3 |
477-2,562 899 |
994-2,353 1,455 |
0.1-0.03 0.1 |
35-245 95 |
99 |
93 |
|
Cu, mg/l |
0.001 |
1.0 |
4.6-12 11 |
16-29 19 |
0.01-0.01 0.01 |
0.9-1.3 1.0 |
99 |
93 |
|
Zn, mg/l |
0.01 |
5.0 |
54-151 121 |
234-397 280 |
0.03-0.2 0.1 |
54-123 107 |
99 |
62 |
|
Mn, mg/l |
0.01 |
0.1 |
8-56 39 |
44-137 82 |
0.1-0.2 0.2 |
1.6-73 34 |
99 |
52 |
|
Cd, mcg/l |
5 |
1 |
40-100 100 |
Not defined |
0.8-5 0.8 |
Not defined |
99 |
– |
|
Cl, mg/l |
300 |
350 |
34-52 42 |
32-53 33 |
23-32 28 |
10-28 20 |
– |
– |
|
SO4, mg/l |
100 |
500 |
2,685-8,791 7110 |
3,710-10,450 7,493 |
583-826 704 |
274-5,460 2133 |
90 |
71 |
|
Dry residue, mg/l |
– |
1000 |
4,356-15,990 11,188 |
14,183-19,942 1,654 |
930-1,284 628 |
458-9,296 4,557 |
– |
– |
|
Zc |
|
|
36,057 |
64,821 |
44 |
15,967 |
|
|
* For reservoirs of fishery importance (Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated December 13, 2016 N 552 “On approval of water quality Standards for aquatic bodies of fishery importance, including standards for maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances in the waters of aquatic bodies of fishery importance”, as amended on August 22, 2023).
** For centralized drinking water supply systems (SanPiN 1.2.3685-21 “Hygienic standards and requirements for ensuring the safety and (or) harmlessness of environmental factors to humans”, as amended on December 30, 2022).
*** The numerator has the minimum and maximum values, and the denominator has the median value.
Table 2
Kurlov's formula
|
Mine |
Unloading AMD |
Discharge (mouth of the Yelchevka and Levikha rivers) |
|
Degtyarskii |
$$ $$
|
$$ $$
|
|
Levikhinskii |
$$ $$
|
$$ $$
|

Fig.3. Durov diagram – graph of the chemical composition of water in the AMD unloading zone and after purification, %-eq/l
As can be seen from Fig.3, in terms of cationic and anionic compositions, most points form compact fields, which indicates the similarity of the chemical composition of water at the two objects. According to the cationic composition in the AMD discharge zone at the Degtyarskii mine, most samples do not have a constant content of elements, unlike Levikhinskii. Sulfate is noticeably predominant in the anionic composition at facilities both in the unloading zone and after discharge. It is important to note that at the discharge of purified AMD at two sites the pH increases and minera-lization decreases. Therefore, based on these two parameters, one can conclude about the effectiveness of the ongoing measures to collect AMD neutralization.
Nevertheless, the metal content in mine waters exceeds the MPC by several orders of magnitude. The most significant (thousands of times) are noted for copper, iron, zinc, aluminum, and manganese at the Levikhinskii mine. On Degtyarskii, there are fewer exceedances for the same elements (Table 3). In general, the mineralization and content of the main polluting components at Levikhinskii is 1.5-3 times higher than in the mine waters of the Degtyarskii mine. To reduce the environmental burden on the hydrosphere and prevent the entry of untreated acidic waters into watercourses at flooded mines, a two-stage AMD purification system operates, which includes neutralization of mine waters with lime milk and sedimentation in a clarifier pond.
Table 3
Exceedances of MPC for reservoirs of fishery importance
|
Mine |
Unloading AMD |
Discharge (mouth of the Yelchevka and Levikha rivers) |
|
Degtyarskii |
Cu (3600) Fe (2790) Mn (1600) Zn (1960) Al (1275) Co (53) Ni (25) Cd (8) Be (8) |
Mn (20) Cu (10) Zn (10) |
|
Levikhinskii |
Cu (16300) Fe (12900) Zn (12700) Al (12350) Mn (5830) Co (110) Ni (50) Cd (50) Be (32) |
Mn (1437) Zn (444) Cu (256) Al (110) Fe (10) Mg (5) Ca (5) Cd (3) Co (3) |
Note. The chemical composition of water is presented in the form of a generalized association, where to the right of the name of the element is the multiplicity of exceeding the MPC for reservoirs of fishery importance.
The estimated acidity of mine waters at the Degtyarskii mine is 1003 mg/l equivalent of CaCO3, at the Levikhinskii mine – 5413 mg/l (Table 4). Consequently, the amount of reagent required to neutralize mine waters differs and according to the calculated data is 1581 and 5462 t/year, respectively (with discharge flow values of 50 and 32 l/s).
Table 4
Calculation of the acidity of mine waters and the amount of lime required for neutralization
|
Mine |
pH, units |
Fe2+, mg/l |
Fe3+, mg/l |
Al, mg/l |
Mn, mg/l |
Cu, mg/l |
Zn, mg/l |
Calculated acidity, mg/l СаСО3 |
Required amount of reagent, t/year |
|
Degtyarskii |
2.5 |
274.4 |
5.6 |
51 |
16 |
3.6 |
19.6 |
1003 |
1581 |
|
Levikhinskii |
3.8 |
1254 |
36 |
494 |
58.3 |
16.3 |
127 |
5413 |
5462 |
After clarification in the Yelchevskii clarifier pond at the mouth of the Yelchevka River, the waters are characterized as magnesium-calcium sulfate, pH is 7.2-7.5, which corresponds to a neutral medium, mineralization is 0.9-1.3 g/l. The concentration of cadmium decreases to 0.0008 mg/l, but remains almost an order of magnitude higher than the MPC for drinking purposes. The iron concentrations at the discharge usually do not exceed 0.1 mg/l, which is significantly lower than the MPCfi (see Table 1).
After clarification in the Levikhinskii clarifier pond at the mouth of the Levikha River, the water composition is also magnesium-calcium sulfate. The hydrogen index varies 6.6-7.6, which indicates a neutral environment. Mineralization – 0.5-9.3 g/l. The efficiency of the two-stage mine water purification system at the Degtyarskii mine reaches 99 % for iron, copper, zinc, manganese and cadmium, and 90 % for sulfate ion (see Table 1). Despite a sufficiently high degree of purification, the concentrations of components at the discharge from the clarifier pond exceed the MPC for reservoirs of fishery importance (MPCfi): manganese (20 times), copper and zinc (10 times), sulfate ion (7 times). According to the normative indicators for drinking water supply, exceedances were found for manganese (2 times) and sulfate ion (1.5 times).
The Levikhinskii mine uses the same purification scheme in general, but it turns out to be much less effective: from 59 % for manganese to 93 % for iron and copper. As a result, in the mouth of the Levikha River at the discharge into the Tagil River, the concentrations of components have significant exceedances of MPCfi: for zinc by 11 thousand times, manganese by 1.4 thousand times, zinc, copper, aluminum – by hundreds of times.
Thus, despite the same AMD purification schemes at the facilities under consideration, the concentrations of pollutants at the discharge into the hydraulic network have different indicators. This can be explained by several factors. Firstly, despite the lower pH values, the acidity of mine waters at the Degtyarskii mine is 5 times lower (see Table 4). Secondly, ponds built in the 1950s, which have been operating without purification for decades, are used to settle water after neutralization. At the same time, the quality of purified water at the Degtyarskii mine is much higher than at Levikhinskii. This is due to the fact that the pond area at the Degtyarskii mine is 1.5 times larger, and its volume is almost 3 times larger. The degree of filling of ponds with sludge after neutralization also varies: 74 % at Yelchevskii and 93 % at Levikhinskii ponds. As a result, the volume of the Yelchevskii pond, which is free for settling, turns out to be 10 times larger. It is obvious that the remaining volume of the Levikhinskii clarifier pond is not enough to settle the water after neutralization and interaction of pollutants with reagents. Thirdly, the stage of passive purification includes sedimentation of water after neutralization in watercourses, the travel time from the neutralization station to discharge is 2.25 times longer at the Degtyarskii mine (Table 5, fig.4).
As a result, according to the total pollution indicator, the degree of purification at the Degtyarskii mine is 300 times higher than at Levikhinskii (despite the fact that this indicator differs only twice in the AMD discharge zone).
Table 5
AMD Cleaning Options
|
Mine |
Consump-tion, l/s |
Characteristics of the clarifier pond |
Passive cleaning sites, km |
Total pollution indicator Zc |
||||||
|
Area, ha |
Volume*, million m3 |
Degree of filling, % |
Free volume, million m3 |
Length**, km |
Time, day |
Unloading AMD |
Discharge |
|
||
|
Degtyarskii |
50 |
220 |
9.34 |
74 |
2.43 |
6.3 (5.0 + 1.3)*** |
1.26 |
36057 |
44 |
|
|
Levikhinskii |
32 |
142 |
3.30 |
93 |
0.23 |
2.8 (0.5 + 2.3) |
0.56 |
64821 |
15967 |
|
|
Multiplicity of parameters |
1.56 |
1.55 |
2.83 |
0.80 |
10.57 |
2.25 |
2.25 |
0.56 |
0.003 |
|
* Project-based. ** General. *** In brackets “neutralization – clarifier” + “clarifier – discharge”.
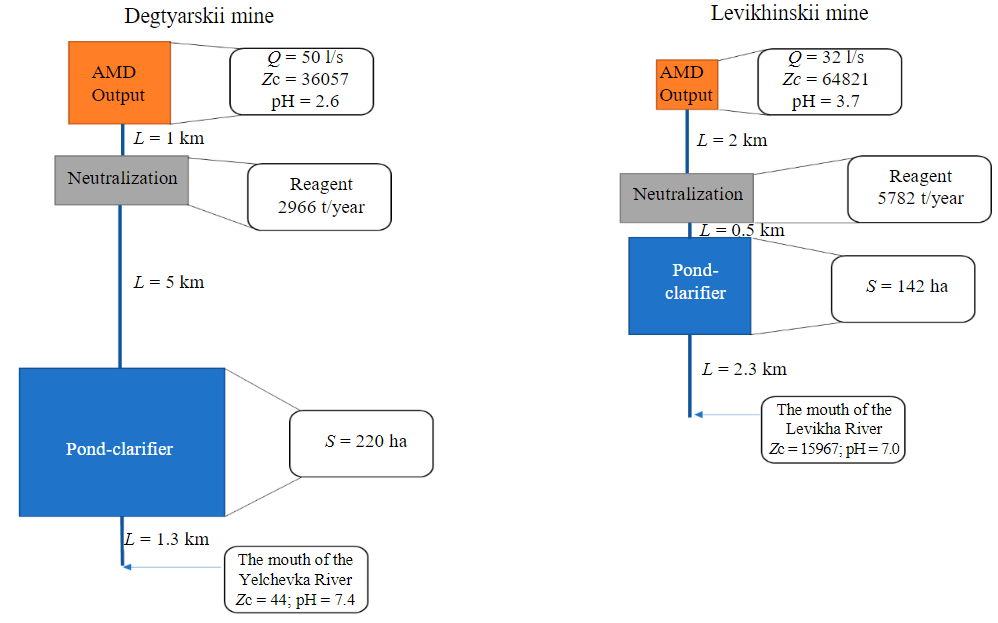
Fig.4. AMD cleaning scheme and parameters
Proposals for the organization of cleaning at the Levikhinskii mine. For the Degtyarskii mine, the current two-stage system is quite effective. For the Levikhinskii mine, it is necessary to switch to the use of more modern systems that include three stages of purification, for example: 1 – sewage treatment plants with aerators, 2 – radial settling tanks, 3 – a cascade of ponds [10].
The first stage of purification is the use of wastewater treatment plants with aerators (for example, FUCHS OxyStar Aerators), which have successfully proven themselves in various enterprises over the past decades. One example of an identical water composition (Fe content up to 700 mg/l) with a low pH value and a flow rate of up to 3,600 m3/h is the output of AMD from a coal mine in Germany4. Aerators are used to supply oxygen to water. In addition to fine bubble deep aeration, they also ensure circulation and thorough mixing of mine waters with the reagent. During operation, aerators draw atmospheric air through a hollow shaft and release it into a stream of water created by a rotating propeller. Due to high turbulence, fine bubble aeration and excellent oxygen transfer efficiency are achieved. When using wastewater treatment plants with aerators (stage 1), the pH of the mine water will increase. As a result of an increase in the mixing rate and the interaction time of acidic waters with lime milk, a precipitate is formed.
According to the results of operation of FUCHS aerators, it was found that purification has an efficiency of 99 % (Mn content from 600 mg/l at the inlet and up to 3 mg/l at the outlet). However, AMD neutralization due to aeration is limited. To achieve a high rate of chemical reactions, increase the efficiency of water purification and reduce the number of aerators, it is possible using a radial type sump with an integrated flocculation chamber (stage 2). Flocculants, when mixed with purified mine waters, will lead to normalization of the pH of the water and its additional purification.
Nevertheless, it is advisable to supplement the active cleaning system with passive cleaning (stage 3). It can be implemented in the form of a cascade of ponds on the section of the riverbed of the Levikha River.
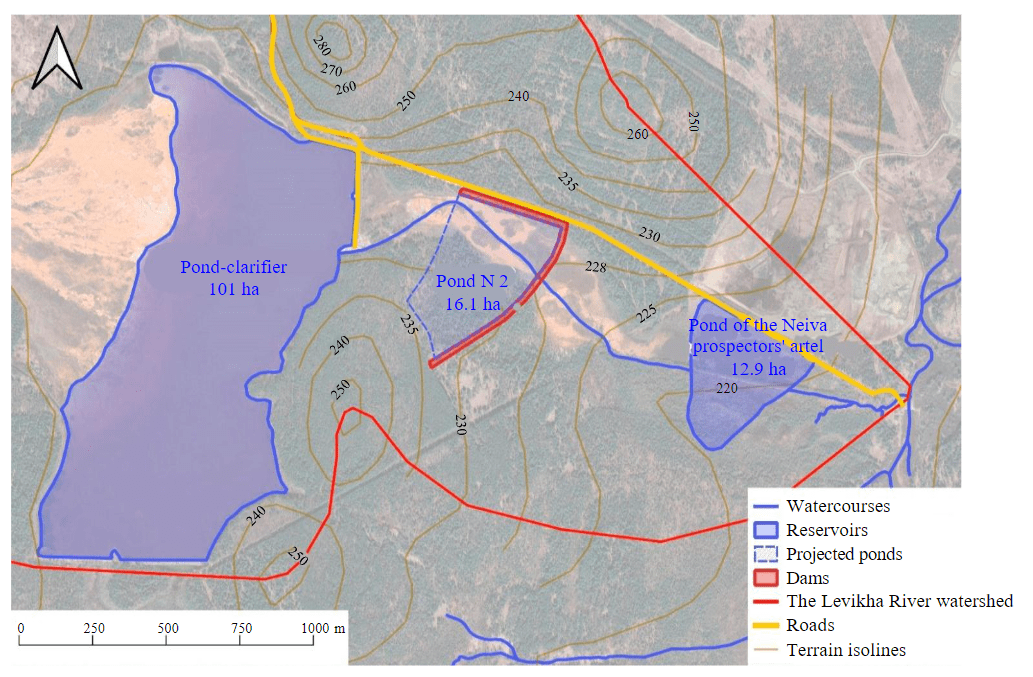
Fig.5. The layout map of the cascade of ponds-clarifiers in the valley of the Levikha River
Since December 2020, the clarifier pond of the Neiva prospectors' artel (a worked out pit with an area of 12.9 ha) located below the main clarifier pond has been included in the main process of mine water purification at the Levikhinskii mine (Fig.5).
In 2021, the concentrations of components at the discharge in the Tagil River decreased significantly compared to the same period in 2020: copper to 0.04-0.5 mg/l (it was 2.2-4.9 mg/l), iron to 0.6-17 mg/l (it was 27-101 mg/l), zinc to 10-20 mg/l (it was 35-96 mg/l), manganese up to 12-16 mg/l (it was 13-38 mg/l), sulfate up to 1515-2115 mg/l (it was 1420-2450 mg/l). Nevertheless, when discharged into the water of the Levikha River, significant exceedances of MPCfi remain: zinc by 1000-2000 times, manganese by 1230-1600 times, copper by 50-500 times, iron by 6-170 times, sulfate ion by 15-21 times (Table 6).
Table 6
Efficiency of mine water purification using the Neiva pond
|
Month |
Year |
Object/indicator |
Components, mg/l |
|||||
|
Cu |
Fe |
Zn |
Mn |
SO4 |
|
|||
|
MPCfi |
||||||||
|
0.001 |
0.1 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
100 |
|
|||
|
March |
2020 |
The multiplicity of MPCThe mouth of the Levikha River |
4,900 |
1,010 |
9,600 |
3,800 |
22 |
|
|
2021 |
400 |
8 |
2,000 |
1,230 |
21 |
|
||
|
2020 |
Cleaning efficiency, % |
67 |
90 |
40 |
32 |
53 |
|
|
|
2021 |
98 |
99 |
91 |
78 |
67 |
|
||
|
April |
2020 |
The multiplicity of MPCThe mouth of the Levikha River |
2,200 |
367 |
3,940 |
1,320 |
14 |
|
|
2021 |
500 |
170 |
1,900 |
1,600 |
20 |
|
||
|
2020 |
Cleaning efficiency, % |
90 |
96 |
82 |
74 |
– |
|
|
|
2021 |
97 |
99 |
88 |
71 |
66 |
|
||
|
May |
2020 |
The multiplicity of MPCThe mouth of the Levikha River |
4,900 |
2,700 |
6,500 |
2,600 |
25 |
|
|
2021 |
50 |
6 |
1,000 |
1,300 |
15 |
|
||
|
2020 |
Cleaning efficiency, % |
71 |
97 |
62 |
62 |
51 |
|
|
|
2021 |
99 |
99 |
95 |
78 |
81 |
|
||
The use of a second clarifier pond compared to the same period in 2020 led to an increase in purification efficiency for iron 99 % (was 90-97 %), copper 97-99 % (was 67-90 %), zinc 88-95 % (was 40-80 %), manganese 71-78 % (was 32-62 %) and sulfate ion 66-81 % (it was 51-53 %). The use of an additional pond can significantly reduce the concentration of elements.
As a result of the accumulation of large volumes of bottom sediments and a high degree of filling of the existing clarifier pond at the Levikhinskii mine, the issue of sludge disposal is relevant. The main areas of sludge use are considered in [35]: reclamation of waste rock dumps and substandard ores, storage in spent quarries, production of building materials, extraction of valuable components and storage after sludge dewatering in geotubes (Geotube). Unfortunately, each of the options has significant limitations. The option of using sludge as a landfill reclamation is not advisable due to the possibility of leaching elements of hazard classes 2-4 from bottom sediments. The laying of worked out pits is impossible due to the fact that the reserves of the field are still listed in the state balance sheet. To implement the option for the production of building materials, it is necessary to organize a public-private partnership. The extraction of valuable components has not yet been provided with cost-effective technology. In addition, the sludge will still need to be stored in geotubes after dewatering. The main limitation is the formation of waste after the extraction of valuable components, the preparation and waterproofing of the site, the construction of extraction plants and the need for significant alienation of land.
Thus, none of the considered options for sludge purification fully allows cleaning the clarifier pond and it is impossible to achieve regulatory indicators at the discharge in the Tagil River without changing the existing purification system.
A further increase in the degree of purification can be achieved using a cascade of ponds and the decommissioning of an existing clarifier pond (Fig.5, Table 7).
Table 7
Estimated cleaning efficiency, %
|
Degrees of purification |
Cleaning system |
Cleaning efficiency |
|
1 |
Sewage treatment plants with aerators |
90-99 |
|
2 |
Radial sump |
80-95 |
|
3 |
Cascade of ponds |
76-100 |
It is not enough to operate only the existing clarifier pond of the Neiva prospectors' artel for passive cleaning due to its small area (12.9 ha). For full-fledged passive cleaning, the area of ponds calculated according to the formula (4) is 18 ha. It is advisable to use the Neiva prospector’s pond and add another clarifier pond with an area of 16.1 ha, which together will ensure the deposition of metals due to a decrease in the water flow rate and an increase in the time of interaction of pollutants with reagents.
Conclusion
AMD is being unloaded to the surface at spent and flooded copper ore mines. The waters are characterized by low pH values (2.5 at Degtyarskii and 3.3 at Levikhinskii mines), the composition of the waters is sulfate, aluminum-iron-calcium-magnesium with mineralization up to 12 g/l.
AMD purification at the facilities under consideration is carried out in two stages: neutralization with lime milk and settling in clarification ponds. The efficiency of mine water treatment at the Degtyarskii mine reaches 99 % for the main pollutants. The Levikhinskii mine uses the same purification scheme in general, but it turns out to be much less effective – from 59 % for manganese to 93 % for iron and copper.
Despite the same purification system, at the Levikhinskii mine, the quality of water discharged into the hydraulic network does not reach the standard indicators, the multiplicity of excess reaches hundreds and thousands for manganese, copper, zinc, aluminum.
The reasons for the low cleaning efficiency at the Levikhinskii mine are a complex of natural and man-made factors:
- despite the lower pH values, the acidity of mine waters at the Degtyarskii mine is five times lower;
- ponds built in the 1950s are used to settle the water after neutralization. They have been working without cleaning for decades. The area and volume of the Yelchevskii pond is 1.5-3 times larger. The degree of filling of ponds with sludge after neutralization is 74 % in the Degtyarskii and 93 % Levikhinskii mines. As a result, the volume of the Yelchevskii pond, which is free for settling, turns out to be 10 times larger;
- the settling time of water after neutralization in watercourses at the Degtyarskii mine is 2.25 times longer.
As a result, according to the total indicator of Zc pollution, the degree of purification at the Degtyarskii mine is 300 times higher than at Levikhinskii (despite the fact that this indicator differs only twice in the AMD unloading zone).
To increase the efficiency of the purification process, it is necessary to modernize the existing system: firstly, to decommission the existing clarifier pond, and secondly, to use active (aerators, radial settling tanks) and passive (cascade of ponds below the discharge of neutralized wastewater) purification systems. Three-stage purification (including structures with aerators, radial settling tanks and a cascade of ponds) will reduce surface water pollution to normalized levels, significantly improve the environmental situation and reduce damage to the hydrosphere.
References
- Alekseyev V.A. Reasons for the Formation of Acidic Drainage Water in Dumps of Sulfide-Containing Rocks. Geochemistry International. 2022. Vol. 60. N 1, p. 78-91. DOI: 10.1134/S0016702922010025
- Rybnikova L.S., Rybnikov P.A. Regularities in the Evolution of Groundwater Quality at Abandoned Copper Sulfide Mines at the Levikha Ore Field, Central Urals, Russia. Geochemistry International. 2019. Vol. 57. N 3, p. 298-313. DOI: 10.1134/S0016702919030091
- Mugova E., Molaba L., Wolkersdorfer C. Understanding the Mechanisms and Implications of the First Flush in Mine Pools: Insights from Field Studies in Europe’s Deepest Metal Mine and Analogue Modelling. Mine Water and the Environment. 2024. Vol. 43. Iss. 1, p. 73-86. DOI: 10.1007/s10230-024-00969-3
- Pshenichny I. Models and methods of geochemical assessment of the risk of interaction of rock dumps with environmental factors. Transbaikal State University Journal. 2022. Vol. 28. N 3, p. 21-27 (in Russian). DOI: 10.21209/2227924520222832127
- Pashkevich M.A., Alekseenko A.V., Nureev R.R. Environmental damage from the storage of sulfide ore tailings. Journal of Mining Institute. 2023. Vol. 260, p. 155-167. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2023.32
- Kharko P.A., Matveeva V.A. Bottom Sediments in a River under Acid and Alkaline Wastewater Discharge. Ecological Engineering & Environmental Technology. 2021. Vol. 22. Iss. 3. P. 35-41. DOI: 10.12912/27197050/134870
- Karagodin S.S., Karagodin V.S., Morozov Yu.P., Zauzolkov I.V. To the question about prospects (upcycle) of abandoned copper-sulphide pits in the Urals. News of the Ural State Mining University. 2018. Iss. 4 (52), p. 114-121. DOI: 10.21440/2307-2091-2018-4-114-121
- Muravyov M., Radchenko D., Tsupkina M. et al. Old Sulfidic Ore Tailing Dump: Ground Features, Mineralogy, Biodiversity – A Case Study from Sibay, Russia. Minerals. 2024. Vol. 14. Iss. 1. N 23. DOI: 10.3390/min14010023
- Sengupta M. Environmental Impacts of Mining. Monitoring, Restoration, and Control. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2021, p. 374. DOI: 10.1201/9781003164012
- Rybnikova L.S., Rybnikov P.A., Navolokina V.Y. Reducing Negative Impacts of Dormant Pyrite Copper Ore Mine on the Geosphere in the Urals. Journal of Mining Science. 2022. Vol. 58. Iss. 3, p. 519-525. DOI: 10.1134/S1062739122030188
- Barabanova E.A. Reservoirs in the Drainage Basins of Russian Arctic Seas. Water Resources. 2019. Vol. 46. N 2, p. 143-151. DOI: 10.1134/S0097807819020027
- Rybnikova L.S., Rybnikov P.A. Assessment of hydrosphere formation factors in nature-and-technology systems: A case-study of the upstream basin of the Tagil River in the Sverdlovsk Region. Mining Informational and Analytical Bulletin. 2021. N 5-2, p. 257-272 (in Russian). DOI: 10.25018/0236_1493_2021_52_0_257
- Davydov V.A. Study of the technogenesis of the Degtyarsky mine by audio-magnetotelluric express sounding. Journal of Mining Institute. 2020. Vol. 243, p. 379-387. DOI: 10.31897/PMI.2020.3.379
- Guman O.M., Makarov A.B., Antonova I.A., Hasanova G.G. Ecological and hydrochemical features of modern technogenic water bodies (on the example of the Ural region). Proceedings of Voronezh State University. Series: Geology. 2018. N 1, p. 148-154. DOI: 10.17308/geology.2018.1/1469
- Makarov A.B., Antonova I.A., Khasanova G.G. Heavy metals in the components of man-made reservoirs of the Ural region. Vestnik Uralskogo otdeleniya Rossiiskogo mineralogicheskogo obshchestva. 2017. N 14, p. 81-86 (in Russian).
- Fedorova O.I. Geoelectrical monitoring of the Yelchevsk soil dam by method of frequency dispersion of electrical resistivity. Uralskiy geofiziceskiy vestnik. 2020. N 2 (40), p. 37-44 (in Russian). DOI: 10.25698/UGV.2020.2.4.37
- Fyodorova O.I., Davydov V.A. Diagnostics of Ground Water-Work Facilities with Electric and Seismic Methods with the Elchevsk Dam as a Study Case. Water Sector of Russia. 2014. N 6, p. 44-55 (in Russian).
- Popov A.N., Pavluk T.Y., Mukhutdinov V.F. Investigation of a Water Body Status to Select Priority Actions on Ecological Rehabilitation (the Volchikha Reservoir as a Study Case). Water Sector of Russia. 2019. N 4, p. 170-195 (in Russian). DOI: 10.35567/1999-4508-2019-4-8
- Kruse Daniels N., LaBar J.A., McDonald L.M. Acid Mine Drainage in Appalachia: Sources, Legacy, and Treatment. Appalachia’s Coal-Mined Landscapes. Cham: Springer, 2021, p. 193-216. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-57780-3_8
- Acharya B.S., Kharel G. Acid mine drainage from coal mining in the United States – An overview. Journal of Hydrology. 2020. Vol. 588. N 125061. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125061
- Maksimovich N.G., Pyankov S.V. Kizelovsky coal basin: environmental problems and solutions. Perm: Raritet-Perm, 2018, p. 288 (in Russian).
- Wolkersdorfer С. Mine Water Treatment – Active and Passive Methods. Springer, 2022, p. 328. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-662-65770-6
- Yongwei Song, Zehao Guo, Rui Wang et al. A novel approach for treating acid mine drainage by forming schwertmannite driven by a combination of biooxidation and electroreduction before lime neutralization. Water Research. 2022. Vol. 221. N 118748. DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118748
- Yanan Jiao, Chunhui Zhang, Peidong Su et al. A review of acid mine drainage: Formation mechanism, treatment technology, typical engineering cases and resource utilization. Process Safety and Environmental Protection. 2023. Vol. 170, p. 1240-1260. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.12.083
- Zendelska A., Trajanova A., Golomeova M. et al. Comparison of Efficiencies of Neutralizing Agents for Heavy Metal Removal from Acid Mine Drainage. Journal of Mining and Environment. 2022. Vol. 13. N 3, p. 679-691. DOI: 10.22044/jme.2022.12090.2205
- Saha S., Sinha A. Review on Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage with Waste Materials: A Novel Approach. Global NEST Journal. 2018. Vol. 20. N 3, p. 512-528. DOI: 10.30955/gnj.002610
- Skousen J.G., Ziemkiewicz P.F., McDonald L.M. Acid mine drainage formation, control and treatment: Approaches and strategies. The Extractive Industries and Society. 2019. Vol. 6. Iss. 1, p. 241-249. DOI: 10.1016/j.exis.2018.09.008
- Skousen J. Chapter 29 – Overview of Acid Mine Drainage Treatment with Chemicals. Acid Mine Drainage, Rock Drainage, and Acid Sulfate Soils: Causes, Assessment, Prediction, Prevention, and Remediation. Wiley, 2014, p. 325-337. DOI: 10.1002/9781118749197.ch29
- Kleinmann B., Skousen J., Wildeman T. et al. The Early Development of Passive Treatment Systems for Mining-Influenced Water: A North American Perspective. Mine Water and the Environment. 2021. Vol. 40. Iss. 4, p. 818-830. DOI: 10.1007/s10230-021-00817-8
- Kleinmann R., Sobolewski A., Skousen J. The Evolving Nature of Semi-passive Mine Water Treatment. Mine Water and the Environment. 2023. Vol. 42. Iss. 1, p. 170-177. DOI: 10.1007/s10230-023-00922-w
- Skousen J., Zipper C.E., Rose A. et al. Review of Passive Systems for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Mine Water and the Environment. 2017. Vol. 36. Iss. 1, p. 133-153. DOI: 10.1007/s10230-016-0417-1
- Turingan C.O.A., Cordero K.S., Santos A.L. et al. Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Using a Process Train with Laterite Mine Waste, Concrete Waste, and Limestone as Treatment Media. Water. 2022. Vol. 14. Iss. 7. N 1070. DOI: 10.3390/w14071070
- Rambabu K., Banat F., Pham Q.M. et al. Biological remediation of acid mine drainage: Review of past trends and current outlook. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology. 2020. Vol. 2. N 100024. DOI: 10.1016/j.ese.2020.100024
- Fetisova N.F. Кислотность и щелочность шахтных вод как ключевые показатели для планирования систем очистки. Gornoe ekho. 2022. N 2, p. 32-38 (in Russian). DOI: 10.7242/echo.2022.2.5
- Rybnikova L.S., Rybnikov P.A., Navolokina V.Y. Rehabilitation of man-made formation of abandoned copper pyrite deposits on the example of Levikhinsky mine (Middle Urals). Bulletin of the Tomsk Polytechnic University. Geo Аssets Engineering. 2023. Vol. 334. N 8, р. 137-150 (in Russian). DOI: 10.18799/24131830/2023/8/4089
